Zirconia (ZrO2), Zirconium Oxide

Zirconia, or zirconium oxide (ZrO2), is renowned for its superior strength and toughness among advanced ceramic materials, exhibiting a white crystalline oxide form. Predominantly found as baddeleyite with a monoclinic structure, ZrO2 excels in mechanical resistance, low thermal conductivity, and high-temperature resilience. The addition of Yttria Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) and Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA) enhances its properties, offering improved thermal stability and toughness, making it ideal for extreme conditions. These composites combine ZrO2's chemical resistivity and high mechanical resistance with exceptional thermal expansion and low conductivity, setting a standard for materials capable of withstanding harsh environments.
Zirconia's resistance to crack propagation and corrosion, coupled with its high thermal expansion, makes it perfect for joining ceramics and metals like steel, ensuring durability and performance in diverse applications. Its utility spans across industries, from aerospace to energy, where its ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures and resist corrosive environments is invaluable. Zirconia ceramics, especially when reinforced with YSZ and ZTA, become indispensable in technological advancements and material science, highlighting their significance in modern engineering and design.
More Info About Zirconia
Products | Structures | Specification | Applications | Video | FAQs | Product Brochure
Zirconia Ceramics Structures
Zirconia ceramics, characterized by their exceptional versatility and strength, exhibit fascinating phase transitions across different temperature ranges, attributable to their unique crystal structures. These structures include the monoclinic, tetragonal, and cubic phases, each with distinct properties and implications for the material's application and performance.
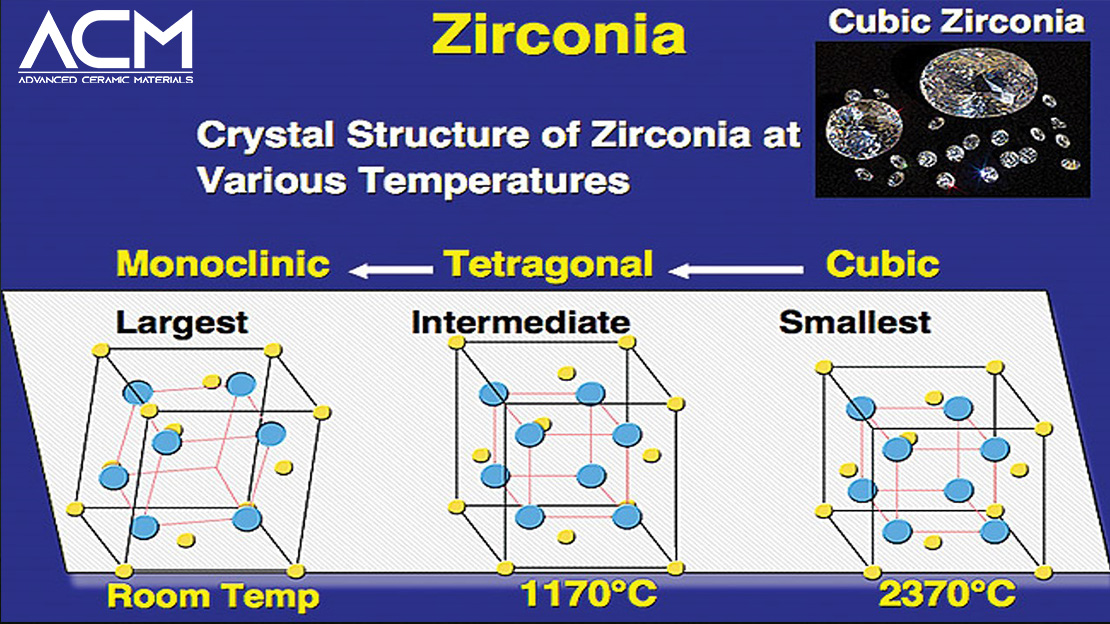
At room temperature, pure zirconia exists in the monoclinic phase (m), which is its most stable form under ambient conditions. This phase is noted for its asymmetrical crystal structure, leading to properties that are beneficial for certain applications requiring high resistance to crack propagation and excellent thermal insulation. However, the monoclinic phase's anisotropic thermal expansion can lead to issues in some applications, necessitating careful control of the material's phase composition depending on its intended use.
As the temperature increases, zirconia undergoes a significant transformation at approximately 1170 °C, transitioning from the monoclinic phase to the tetragonal crystal structure (t). This phase change is accompanied by an increase in symmetry and a reduction in volume, which can induce stress and, potentially, microcracking if not managed correctly. The tetragonal phase, however, is instrumental in the material's renowned toughness, especially when stabilized by the addition of dopants such as yttrium oxide. This stabilization can prevent the material from transforming back to the monoclinic phase upon cooling, thereby exploiting the tetragonal phase's mechanical properties at room temperature.
Further heating leads zirconia to adopt a cubic crystal structure (c) at temperatures above ∼2370 °C, eventually transitioning into a fluorite structure—a high-symmetry, high-density phase that allows for exceptional ionic conductivity. This phase is particularly relevant for high-temperature applications, such as solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and oxygen sensors, where ionic transport is crucial. The cubic phase remains stable up to the melting point of zirconia, which is at an exceedingly high temperature of 2716 °C, underscoring the material's suitability for extreme environments.
Read more: What is Cubic Zirconia?
The ability of zirconia to exist in these three different crystal structures, combined with the phase transitions that occur at specific temperatures, plays a critical role in its application across various industries. By manipulating the phase composition through the addition of stabilizers and controlling the thermal treatment process, engineers and scientists can tailor the material's properties to meet the requirements of a wide range of applications, from cutting-edge aerospace components to advanced medical implants, highlighting the versatility and importance of zirconia ceramics in modern material science.
Zirconia Ceramics Specification
| Material | Zirconia | |
| Properties | Units | ZrO2 |
| Color | - | Ivory & White |
| Permeability | - | Gas-tight |
| Density | g/cm3 | 5.89 |
| Straightness | - | 1‰ |
| Hardness | Mohs Scale | 8.5 |
| Water Absorption | - | 0 |
| Flexural Strength(Typical 20℃) | Mpa | 1200 |
| Compressive Strength (Typical 20℃) |
Mpa | 5700 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (25℃ to 800℃) |
0-6/℃ | 10 |
| Dielectric Strength (5mm Thickness) | AC-kv/mm | - |
| Dielectric Loss 25ºC@1MHz |
- | 0.001 |
| Dielectric Constant | 25º C@1MHz | 29 |
| Volume Resistivity (20℃) (300℃) |
Ω·cm³ | >10^13 5*10^8 |
| Long-term Operating Temperature | ℃ | 2200 |
| Thermal Conductivity (25℃) | W/m·K | 3 |
Zirconia Ceramics Applications
Zirconia ceramics, owing to their exceptional mechanical properties and versatility, find applications in a broad spectrum of fields, ranging from industrial manufacturing to advanced medical procedures. The material's high strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and corrosion make it an ideal choice for the production of hard ceramics. These ceramics are employed in the manufacturing of cutting tools, bearings, and valves, where durability and reliability under stress and high temperatures are paramount.
Read more: Zirconium Oxide Ceramic & Its Uses
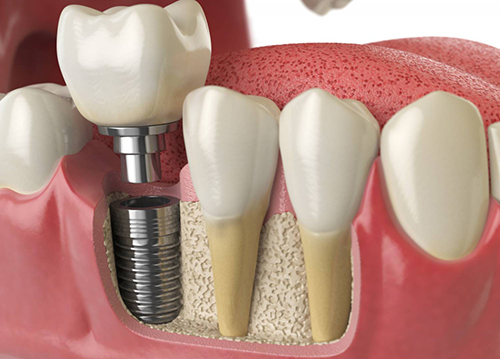
Dental Applications
In the medical field, zirconia's biocompatibility and aesthetic qualities are leveraged for dental crowns and implants. Zirconia crowns, in particular, are chosen for their resemblance to natural tooth enamel, strength, and durability, providing a superior alternative to traditional materials with enhanced cosmetic and functional outcomes.
Read more: How to Use Zirconia in Dentistry?
Oxygen Sensors and Fuel Cell Membranes
Stabilized zirconia is a cornerstone in the development of oxygen sensors and solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) membranes. Its high ionic conductivity at elevated temperatures enables efficient oxygen ion transport, crucial for accurate oxygen measurement and efficient energy conversion in automotive and industrial settings.
Read more: Stabilized Zirconia Used in Oxygen Sensor
Solid Electrolyte in Electrochromic Devices
Zirconia's application as a solid electrolyte in electrochromic devices, such as smart windows and displays, showcases its role in energy-saving technologies. These devices, which change color or opacity in response to an electrical signal, offer the potential for significant advancements in architectural and automotive applications.
Hard Ceramics Production
Zirconia's exceptional mechanical properties, such as high strength and toughness, make it an ideal candidate for hard ceramics production. Utilized in cutting tools, bearings, and valves, zirconia ceramics ensure durability and reliability under high stress and temperatures, critical for industrial manufacturing processes.
Protective Coatings for Pigments
As a protective coating, zirconia enhances the durability and wear resistance of titanium dioxide particles used in pigments. This application is vital for maintaining the pigments' brightness and stability in paints, coatings, and plastics, ensuring their longevity and consistent performance.
Refractory Material
In high-temperature applications, zirconia serves as an excellent refractory material. Its thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock make it suitable for furnaces, kilns, and reactor linings, providing essential insulation and protection against extreme temperatures. Zirconia's hardness also lends itself to abrasive products and enamels, facilitating superior cutting, grinding, and polishing operations.
ACM Ceramic Product Video
Your Zirconia Ceramics Supplier
Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) is a leading supplier of zirconia ceramic products of the highest quality for a wide range of applications. We are happy to provide advice on materials, design, and application. Feel free to contact us with any questions about ZrO2 or other ceramic materials that are not listed on the website.
| Chemical Formula | ZrO2 |
| Mechanical | |
| Density | 6 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 13 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 220 GPa |
| Flexural Strength | 1000 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 5690 MPa |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.31 |
| Fracture Toughness | 4 MPa m½ |
| Electrical | |
| Dielectric Strength | 11 ac V/mm |
| Dielectric Constant | 33 (@ 1 MHz) |
| Volume Resistivity | 10^13 ohm-cm |
| Thermal | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 9.5 x 10^-6/°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 3 W/(m*K) |
| Specific Heat | 0.46 x10^3 J/(Kg*K) |
| Shock Resistance | 300 °C Diff. |
| Maximum Working Temperature | 1000 °C |