Zirconia as a Thermal Insulator in Extreme Environments
In the world of advanced materials, zirconia stands out as a versatile ceramic known for its exceptional properties. Among its many applications, one that particularly shines is its role as a thermal insulator. This quality makes zirconia invaluable in situations where resistance to extreme temperatures is paramount.
Understanding Zirconia's Thermal Insulation Properties
Zirconia, a crystalline oxide of zirconium, boasts remarkable thermal insulating characteristics. In simple terms, it can resist and minimize the transfer of heat. This is important in many industries, from aerospace to manufacturing, where dealing with high temperatures is always a challenge.
Further Reading: Zirconia's Thermal and Electrical Insulation Properties
Zirconia's Composition and Structure
To grasp why zirconia is an effective thermal insulator, it's essential to delve into its composition. Zirconia, also known as zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), has a crystal structure where oxygen atoms are arranged in a pattern with zirconium atoms. This specific arrangement contributes to its excellent thermal insulating capabilities.
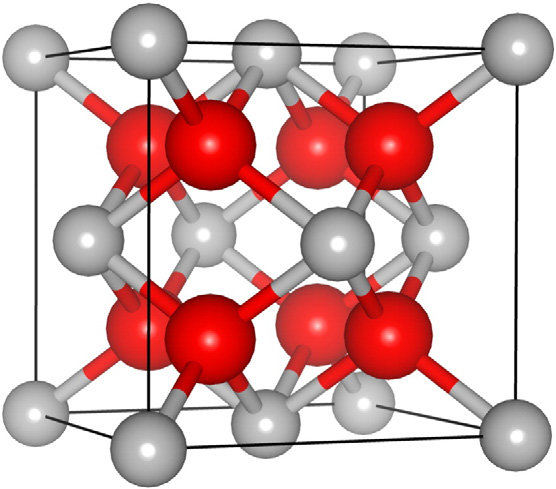
Zirconia in Extreme Environments
Aerospace Applications
One of the key areas where zirconia shines as a thermal insulator is in the aerospace industry. In the harsh environment of space or within the intense heat generated during atmospheric re-entry, materials face extreme conditions. Zirconia-based coatings and components act as protective barriers, preventing excessive heat from affecting sensitive spacecraft structures.
Manufacturing and High-Temperature Processes
In manufacturing, especially in processes involving high temperatures, zirconia finds applications as a crucial thermal insulator. Furnace linings, kiln furniture, and various industrial components benefit from zirconia's ability to withstand and mitigate heat transfer. This not only ensures the longevity of the equipment but also contributes to the efficiency of the overall manufacturing process.
The Manufacturing Process of Zirconia for Thermal Insulation
The intricate process of crafting zirconia with superior thermal insulation properties requires meticulous control and precision. The journey begins with high-purity zirconium oxide powders, which serve as the raw material for this advanced ceramic.

Powder Stabilization with Magnesium and Calcium
To optimize zirconia's thermal insulation capabilities, the zirconium oxide powders undergo a crucial step of stabilization. Elements like magnesium and calcium are carefully introduced into the mix. These stabilizers play a pivotal role in enhancing zirconia's inherent ability to withstand changes induced by high temperatures. The addition of these elements ensures that the final product will possess the desired thermal resistance characteristics.
Controlled Heating at Extreme Temperatures
The next stage of the manufacturing process involves subjecting the stabilized zirconium oxide to controlled heating. This step is conducted in a carefully regulated environment, where temperatures soar to around 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This extreme heat is instrumental in the transformation of the stabilized powder into the crystalline structure of zirconia.
Formation of Heat-Resistant Zirconia Crystals
Under intense heat, the zirconium oxide undergoes a profound metamorphosis, leading to the formation of zirconia crystals with exceptional heat-resistant features. The controlled environment ensures that the crystal lattice structure aligns optimally, granting zirconia its thermal insulation prowess.
Zirconia vs. Other Thermal Insulating Materials
Zirconia vs. Traditional Refractories
When compared to traditional refractory materials, zirconia offers distinct advantages. Traditional refractories, like alumina, may degrade under extreme temperatures. Zirconia's stability and resistance to phase changes make it a superior choice for applications requiring prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Zirconia vs. Thermal Barrier Coatings
Zirconia is used as a protective coating in gas turbine engines, especially as a thermal barrier. Its strength in high temperatures and its low heat conductivity make it a perfect choice for safeguarding vital engine parts. The high degree of thermal insulation provided by zirconia contributes to increased engine efficiency and longevity.
Conclusion
In the realm of advanced ceramics, zirconia emerges as a silent hero, playing a crucial role as a thermal insulator in extreme environments. Its ability to resist heat transfer makes it indispensable in aerospace, manufacturing, and various high-temperature applications. As industries continue to push the boundaries of what materials can endure, zirconia stands tall, providing a shield against the relentless forces of extreme temperatures.
In essence, zirconia's journey from powder to protective coating is a testament to human ingenuity harnessing the inherent properties of materials for technological advancement. As we learn more about space and improve how things are made, zirconia's job as a heat protector will probably grow. This will make it an even more important part of top-notch materials.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments