What Is Zirconia Ceramic Used For?
Introduction
Zirconia ceramics have emerged as a prominent material in advanced ceramics, renowned for their exceptional properties like high-temperature resistance, electrical insulation, and superior wear resistance. These characteristics make zirconia ceramics highly valuable across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, and notably, medical applications. Particularly in the medical field, zirconia ceramics have revolutionized dental prosthetics, offering durability combined with aesthetic appeal. This article delves into the diverse applications and advantages of zirconia ceramics, illustrating why they have become a material of choice for so many industries.
What is Zirconia Ceramic?
Zirconia ceramic, initially utilized in dentistry as a base for prosthetic frameworks, has evolved significantly in its applications. Recognized for its robustness, zirconia is now widely used to create monolithic restorations that require minimal invasive preparation yet offer exceptional durability and aesthetics. Its unique characteristic of being a monochromatic, uniform material allows for customization through color infiltration techniques, making it highly adaptable to the aesthetic needs of patients. Additionally, the innovation in polychromatic CAD/CAM blocks and disks has expanded its use. These developments enable the production of dental restorations that mimic natural teeth with remarkable precision, offering gradients of color that transition smoothly from the dentin to the enamel, enhancing the natural appearance of dental prosthetics.
Classification of Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are versatile and complex, existing in three primary crystalline forms: monoclinic, tetragonal, and cubic. Each form is stable at different temperatures and offers unique properties. Monoclinic zirconia is stable up to 1,170°C, while tetragonal and cubic forms become stable when the temperature exceeds 2,370°C. The transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic zirconia is particularly noteworthy due to its ability to induce a volume increase of approximately 4%, which can close cracks and significantly enhance the material's fracture toughness—a phenomenon known as transformation toughening.
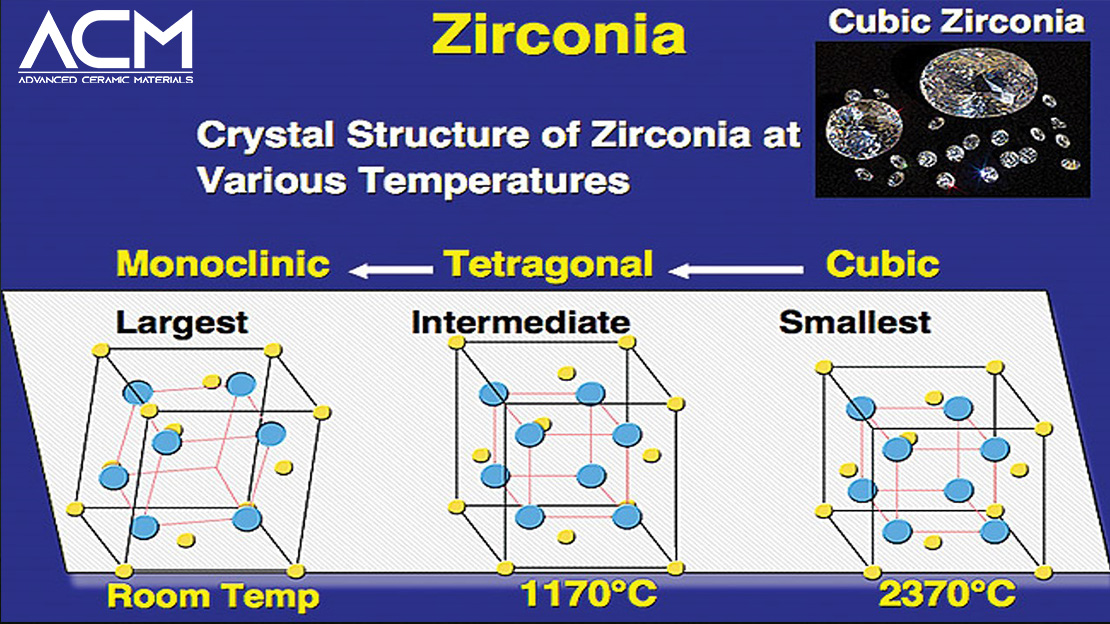
To utilize these properties effectively in various applications, zirconia must be stabilized in the tetragonal or cubic phases at room temperature. This stabilization is achieved through alloying zirconia with oxides such as yttrium oxide (Y2O3), magnesium oxide (MgO), calcium oxide (CaO), and cerium oxide (CeO2). These additives inhibit the transformation back to the monoclinic phase and maintain the material’s toughness and durability at lower temperatures.
Further reading: Yttria vs. Calcia vs. Magnesia: Decoding Stabilized Zirconia Options
Zirconia ceramics are classified based on their phase stability and microstructure:
- Fully Stabilized Zirconia (FSZ): Contains cubic phase throughout and is stabilized with over 8 mol% yttrium oxide, which maintains its structure across a wide temperature range.
- Partially Stabilized Zirconia (PSZ): Features a mixture of monoclinic and tetragonal phases, or tetragonal and cubic phases, offering a balance between toughness and strength.
- Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystals (TZP): Predominantly comprises the tetragonal phase and is usually stabilized with yttria or ceria. TZP materials are highly prized in applications requiring excellent wear resistance and mechanical strength, such as in dental prosthetics.
Each type of stabilized zirconia offers distinct advantages depending on the specific requirements of the application, making zirconia one of the most adaptable and useful ceramic materials available today.
Concentrated Discussion on Zirconia Used in Dentistry
In the field of dentistry, Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystals (TZP) are especially significant due to their high strength and fracture toughness. These properties make TZP an ideal material for dental applications such as crowns and bridges, where durability and aesthetic appearance are crucial. Commonly, Yttria-Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystals (Y-TZP) are used in dental prosthetics due to their superior mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility.
Y-TZP is favored for its ability to withstand the intense stresses that occur within the oral environment, resisting cracking and wear over long periods. Additionally, the aesthetic qualities of Y-TZP are commendable, as it can be made to closely mimic the appearance of natural tooth enamel in terms of color and translucency. This makes Y-TZP a popular choice for front tooth restorations where cosmetic appearance is paramount.
Moreover, the advances in CAD/CAM technology have greatly enhanced the usability and accessibility of zirconia in dental practices. This technology allows for precise customization of dental pieces, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal function. Dentists can now design and manufacture zirconia dental prosthetics that are tailored to the individual contours of each patient’s mouth, providing not only functional benefits but also comfort and natural appearance. This level of customization, combined with the material's durability, makes zirconia ceramics a transformative option in modern dental care, significantly improving patient outcomes.
List of Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics
The market offers a variety of stabilized zirconia ceramics tailored for different dental and industrial applications, each bringing unique benefits to the table. Some notable products include:
- Nobel Procera Zirconia: Known for its precision and strength, Nobel Procera Zirconia is often used in creating durable and aesthetically pleasing dental crowns and bridges.
- Lava/Lava Plus: These zirconia ceramics are praised for their color accuracy and versatility, making them popular choices for cosmetic dental applications.
- In-Ceram YZ: Designed for high-strength frameworks, this material combines the toughness of zirconia with excellent aesthetics.
- Zirkon Zahn Prettau Zirconia: Specially formulated for full-contour zirconia restorations, Prettau Zirconia is highly resistant to chipping and wear.
- Katana Zirconia ML: This multi-layered zirconia provides a gradient of color that mimics natural teeth, ideal for anterior crown restorations.
- Cercon ht: Known for its high translucency, Cercon ht is suitable for creating lifelike dental prostheses that require a natural appearance.
- IPS e.max ZirCAD: Offers an optimal balance of strength and aesthetics, making it a preferred choice for a wide range of dental restorations.
- Zenostar: Noted for its robust mechanical properties and aesthetic qualities, Zenostar zirconia is versatile for both anterior and posterior restorations.
Conclusion
Zirconia ceramic has emerged as a popular material for use in prosthetic dentistry. Its unique properties make it an excellent choice for creating monolithic restorations. Its classification into different types based on its microstructure can help in selecting the appropriate material. Additionally, the availability of different stabilized zirconia ceramics means that clinicians can choose a product that suits their requirements.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}










