What are the Ceramics Used as Heating Elements?

What is a Heating Element?
A heating element is an element or material capable of converting electrical energy to heat energy. This occurs by a process known as Joule heating. In this process, as electrical current flows through an element, electrons collide with the atoms of the element, producing resistance. It is this resistance that gives rise to heat. Therefore, the magnitude of heat energy produced in a heating element depends on the magnitude of the electric current and the resistance of the heating element. It is worth noting that the resistance of the heating element is a more important factor than the electric current. Heating elements can be made from different materials. They can be made from metals such as nichrome and Kantha or ceramics such as silicon carbide and pyrolytic boron nitride. In this article, we'll focus on ceramic heating elements.
Requirements for a Good Ceramic Heating Element
Not all materials can be used as a heating element. What are some pointers that can be used to determine if a material will make a good heating element or not Read further to discover the properties that make good ceramic heating elements stand out.
Electrical Resistance
Heating elements need to have a high degree of electrical resistance to produce heat. This is one of the reasons superconductors cannot be used as heating elements. Although a ceramic heating element needs to have high electrical resistance, the electrical resistance should not be high enough to make the material an electrical insulator. This is because electric current still needs to pass through a heating element.
Resistance to Oxidation
Heat can cause oxidation in materials. Oxidation can destroy a heating material and reduce its efficiency. This implies that oxidation affects the lifespan of heating elements. Hence, a heating element must be resistant to oxidation. To protect ceramic heating elements from the adverse effects of oxidation, you can coat them with silicon oxide or aluminum oxide.
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
Usually, as the temperature rises, resistance in the material does the same. Materials that exhibit a rapid rise in resistance as temperature rises are said to have a high-temperature coefficient of resistance. Heating elements must have a low-temperature coefficient of resistance. However, in instances where the amount of change in resistance can be predicted, a high-temperature coefficient of resistance is ideal. This is because a rapid increase in resistance will deliver more power to the heating material.
Ductility
Heating elements need to be ductile so that they can be easily drawn into wires and manipulated into different shapes without a change in efficiency.
Resistance to Deformation
It is expected that a good ceramic heating element can withstand deformation at very high temperatures.
Melting Point
Ceramic heating elements with high melting points are more efficient than those with low melting points. This is because they can generate a high amount of heat without changing their state. One of the advantages of ceramic heating elements over metallic heating elements is that the former has a high melting point.
Ceramic Materials Used as Heating Elements
Some ceramic materials are well suited for making heating elements. Heating Elements made from these materials are called ceramic heating elements. Here are some materials frequently used in making ceramic heating elements.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
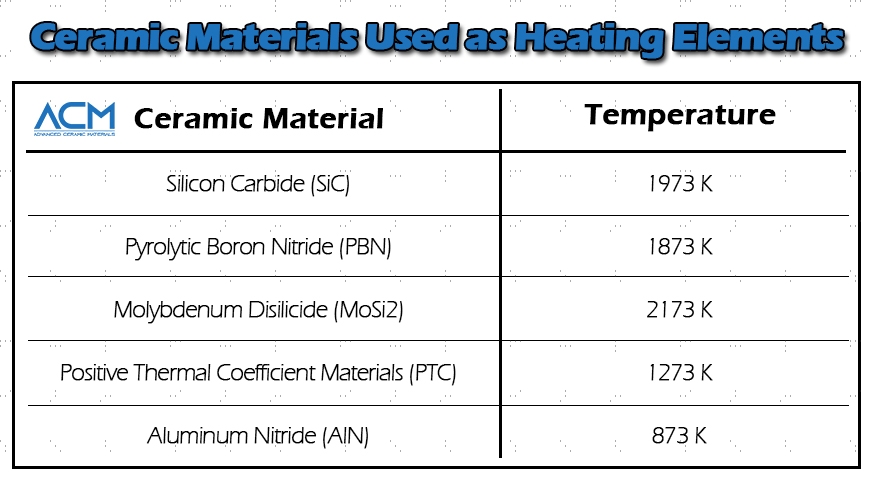
Silicon carbide is another material used in making ceramic heating elements. This material is suitable as a heating element because it does not deform at elevated temperatures and it has a low coefficient of thermal expansion. Furthermore, it is chemically inert and is not prone to corrosion or oxidation. Silicon carbide heating elements can generate heating temperatures of up to 1973 K.
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN)
Both PBN and PG are extremely pure (99.99% or even higher) and very stable in a vacuum or inert atmosphere. The PBN-PG heating element could be very durable and keep the chamber clean. It could be heated to ultra-high 1873K in a very short time without the emission of any gas component. These heating elements are ideal products for the semiconductor industry and applications that require high temperature, high vacuum, and high purity.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
Molybdenum disilicide is a common material for making heating elements. This ceramic-metallic composite has a high melting point and a high oxidation resistance. These properties make it ideal as a heating element in high-temperature furnaces. Molybdenum disilicide heating elements can generate heating temperatures of about 2173 K. It is important to handle these ceramic heating elements with care as they are brittle at room temperature.
Positive Thermal Coefficient Materials (PTC)
With PTC materials, resistance increases to a high degree upon heating. As the name implies, they have a positive thermal coefficient of resistance. This gives PTC materials the ability to act as their own thermostats, regulating the degree to which they heat up. Current does not flow in these materials when they are hot. Typically they can generate heating temperatures of up to 1273 K.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
Aluminum nitride is usually used in the manufacture of advanced ceramic heating elements. Ceramic heating elements made from this material typically have high thermal conductivity and high corrosion resistance. In addition, they heat up faster to 873K and there is even thermal distribution.
Conclusion
Ceramic materials are becoming more popular for making heating elements. Ceramics used in heating elements usually have a high melting point and a high resistance to deformation. These properties make them suitable for application in the production of several essential items, such as hot air dryers, water heaters, industrial baths, etc. For more information about high-quality advanced ceramic materials, please visit https://www.preciseceramic.com/.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}