Boron Nitride Nanosheets Used as Protective Barriers for Metals
Deterioration of Metals
Dangers of Corrosion
Metal corrosion is a common phenomenon that a refined metal is converted into its oxidized form or other compounds, and it may cause lots of trouble. For one thing, deterioration is dangerous for infrastructures - pipes would leak, and buildings would collapse. For another, it takes a large amount of money to prevent or fix corrosion - the United States spends nearly $300 billion on corrosion problems each year [1]. So a variety of methods and materials are employed to protect metals from corrosion.
Ways to Protect the Metal from Corrosion
Several methods are taken to protect metals from design, manufacturing to the utilization of metals:
- Design: Designers are supposed to take corrosive environmental elements like saltwater in advance. Water and debris should be taken from the surface. Narrow gaps should be removed to avoid crevice corrosion.
- Coating: Protective coatings can serve as a layer to protect metals from corrosion elements. A variety of materials including boron nitride nanosheets are used to make protective coatings.
- Environmental Control: Keep metal tools in a clean and dry place, and try to control the level of sulfur, chloride, or oxygen in the long term.
- Cathodic Protection: This method involves using an opposing electrical current on the surface.
- Daily Maintenance: Daily maintenance is as important as the methods discussed above. Please keep your equipment clean.
BN Nanosheets Used as Protective Barriers
What Is a Boron Nitride Nanosheet?
A boron nitride nanosheet is a two-dimensional boron nitride acquired by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and applied to various industries. Boron nitride nanosheets have desirable properties to be used as protective barriers. Similar to graphene, it is quite hard in terms of physical features. But boron nitride nanosheets have stability and dielectric features, which is quite different compared with graphene. Boron nitride nanosheets also stand out for the following properties:
- Thermal stability: Boron nitride nanosheets have better oxidation resistance than graphene, so they become the perfect options to make protective coatings due to their thermal stability and electrical insulation features.
- Electronic insulation: This material is an excellent dielectric substrate, and its insulation feature has little to do with the thickness of boron nitride nanosheets.
- Wide bandgap: BN nanosheets have a wide bandgap of ~5.9 eV, while graphene has none.
Advantages of BN Nanosheets as Protective Barriers
It is rather common to use metal and ceramic coatings to slow metal deterioration. Graphene has been used as the protective coating in the past, but BN nanosheet takes its place with the proper properties listed below:
- BN nanosheet has a wider bandgap, so it appears to be more transparent in visible light.
- BN nanosheet could avoid potential galvanic corrosion for its electronic insulation feature.
Case Study: BN Nanosheets for Copper Foil Protection
Let’s discuss the protective effect of BN nanosheets using a specific case[2]. In this case, a bare copper foil was heated at 250 °C in the open air for 100 hours. The control group employed the same bare metal piece with BN nanosheet coatings. The performance of each group under high temperatures was observed as follows:
- The bare metal foil and the control group with a protective coating appeared in similar metallic color in the beginning.
- Two hours later, black oxidization formed on the surface of the bare copper foil, yet the control group barely changed its color.
- The bare metal piece became orange and even black after continuous heating.
- The oxidization could also be observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy.
The anti-corrosion performance of BN nanosheet protective coating has been proved in detail in this case.
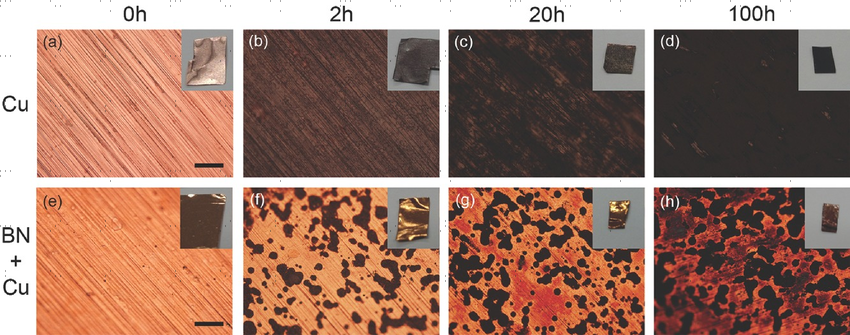
Optical microscopy photos of the bare Cu foil (Cu) and the BN-covered Cu foil (BN+Cu) before (0 h) and after heating at 250 °C in air for 2, 20 and 100 h. For comparison, the exposure time for all the photos is the same. The scale bars are 100 μm. The insets are the corresponding digital camera photos.
Other Applications of BN Nanosheets
The BN materials are extensively used in a range of fields other than making protective coatings.
- BN nanosheet is known for its wide bandgap (~5.9 eV), so it is used in several semiconductors devices, such as transparent membranes, encapsulation materials, and high dielectric materials.
- The thin layer of BN sandwiched between the graphene layers (C-BN-C) serves as a field effect tunneling transistor. BN nanosheet forms a good tunnel barrier as well.
2. Conclusion
Boron nitride nanosheets offer effective protective barriers for metals thanks to their stability and dielectric features. Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) offers high-quality boron nitride nanosheets of various purities and sizes. Please visit https://www.preciseceramic.com/ for more information about BN materials or other related ceramic materials.
Reference
[1] Koch, Gerhardus & Brongers, Michiel & Thompson, N. & Virmani, Y. & Payer, Joe. (2001). Corrosion Cost and Preventive Strategies in the United States.
[2] Li, Luhua & Xing, Tan & Chen, Ying & Jones, Robert. (2014). Boron Nitride Nanosheets for Metal Protection. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 1. 10.1002/admi.201300132.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}










