Crucibles in Focus: A Comparative Analysis of Price, Operating Temperature, and Materials

Introduction:
Crucibles play a pivotal role in various industrial and laboratory processes, serving as containers for melting and processing materials at high temperatures. The choice of crucible material is a critical decision, influenced by factors such as operating temperature, the type of materials to be processed, and budget considerations. In this article, we will delve into a detailed comparative analysis of ten popular crucible materials, with a focus on price, operating temperature, and suitable applications.
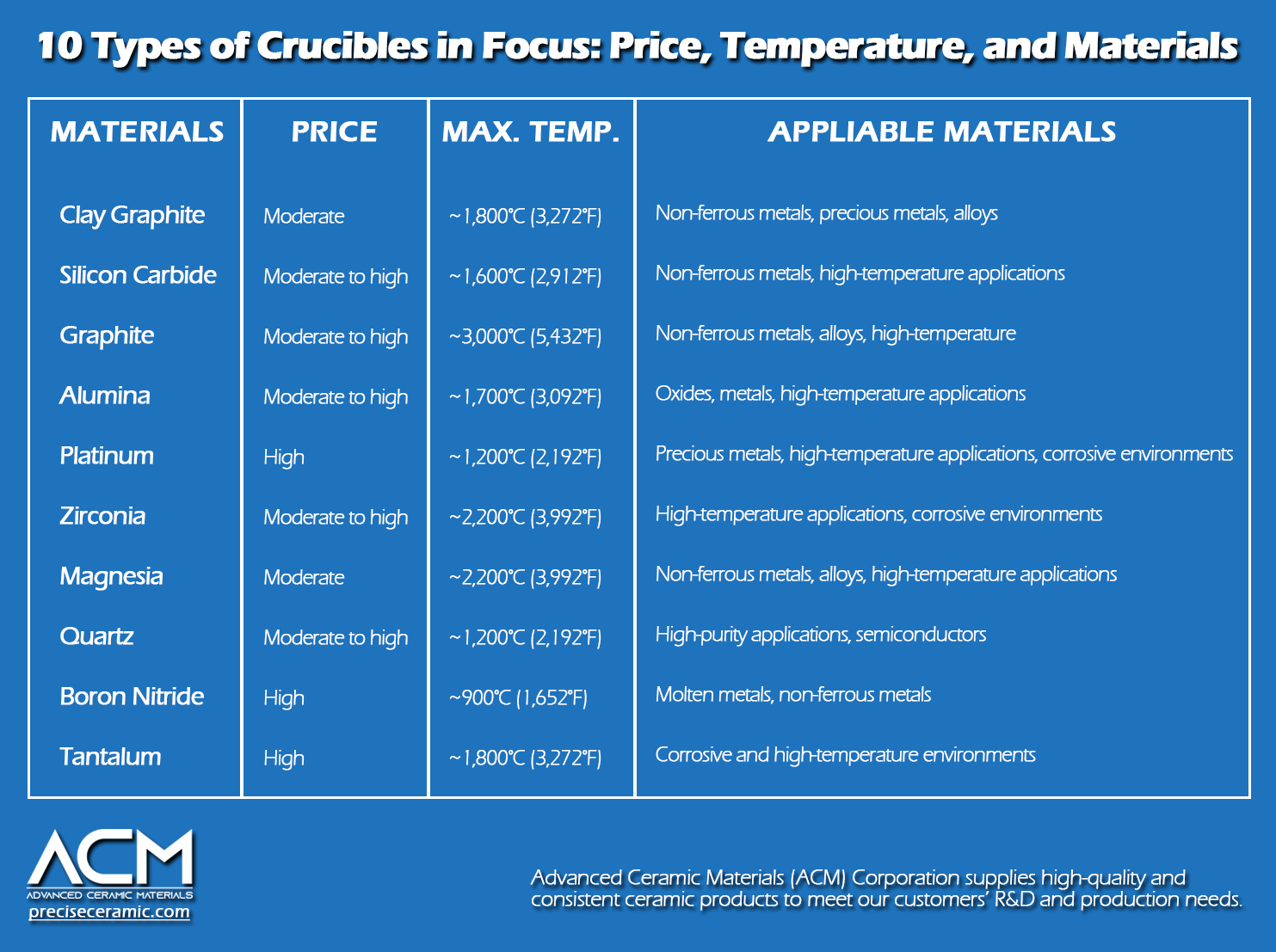
10 Popular Crucible Materials and Their Features
1. Clay Graphite:
Clay graphite crucibles strike a balance between affordability and versatility. With a moderate price range, these crucibles boast an impressive operating temperature of up to 1,800℃ (3,272°F). They find application in the processing of non-ferrous metals, precious metals, and alloys. Their adaptability and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for a wide range of industrial and laboratory settings.
2. Silicon Carbide:
Silicon carbide (SiC) serves as an excellent crucible material due to its remarkable high-temperature resistance, thermal conductivity, and thermal shock resistance. Silicon carbide crucibles offer excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock.
While they come with a moderate to high price tag, their operating temperature reaches up to 1,600°C (2,912°F). This makes them well-suited for applications involving non-ferrous metals and high-temperature processes. The investment in silicon carbide crucibles pays off with their durability and reliability, especially in environments with rapid temperature changes.
3. Graphite:
Graphite crucibles are known for their high operating temperatures, reaching up to 3,000°C (5,432°F). With a moderate to high price range, these crucibles find utility in processing non-ferrous metals, alloys, and high-temperature applications. The versatility of graphite, combined with its thermal shock resistance, makes it a preferred choice for various melting and processing needs.
4. Alumina:
Alumina, or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), excels as a crucible material due to its favorable combination of properties. With a moderate to high price range, alumina crucibles exhibit remarkable thermal stability, maintaining their structural integrity up to temperatures of 1,700°C (3,092°F). The material's high resistance to thermal shock makes it reliable in applications involving rapid temperature changes.
Alumina is chemically inert, ensuring minimal reactivity with molten metals and enabling the production of pure final products. Its versatility extends to applications with oxides, metals, and high-temperature processes. Alumina crucibles strike a balance between cost and performance, making them a common choice in laboratories and industries where specific material properties and durability are paramount.
5. Platinum:
Platinum crucibles, though expensive, are unparalleled in certain applications. With an operating temperature of up to 1,200°C (2,192°F), these crucibles are ideal for handling precious metals and high-temperature processes. Their resistance to corrosion makes them well-suited for harsh environments. While the cost is a significant factor, the unique properties of platinum crucibles justify their use in specialized applications.

Read more: How to Maintain Platinum Crucible
6. Zirconia:
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), stands out as a valuable crucible material, particularly in settings with high temperatures and corrosive conditions. Falling within a moderate to high price range, zirconia crucibles boast an impressive operational temperature of up to 2,200°C (3,992°F), catering to applications that demand exceptional heat resistance. Their resistance to corrosive substances makes them suitable for environments where other materials might succumb to chemical attack.
Zirconia's durability, combined with its ability to withstand thermal and mechanical stresses, positions it as a robust choice for the melting and processing of diverse materials. Its chemical stability and resistance to thermal shock enhance the reliability of zirconia crucibles in crucial industrial processes, justifying their use in situations where performance under harsh conditions is of utmost importance.
7. Magnesia:
Magnesia, composed of magnesium oxide (MgO), presents itself as a favorable crucible material, particularly valued for its versatility and moderate cost. With an operating temperature of up to 2,200°C (3,992°F) and a moderate price range, magnesia crucibles find application in processes involving non-ferrous metals, alloys, and high temperatures.
Their adaptability and durability make them a popular choice in various industrial and laboratory settings, where a balance between cost and performance is crucial. Magnesia crucibles exhibit resistance to thermal and mechanical stresses, providing reliability during repeated heating and cooling cycles. Additionally, their moderate price makes them an economically viable option for applications that require robust crucibles without compromising on budget considerations.
8. Quartz:
Quartz crucibles, with a moderate to high price range, are designed for high-purity applications, particularly in the semiconductor industry. With an operating temperature of up to 1,200°C (2,192°F), quartz crucibles provide a clean and controlled environment for materials requiring stringent purity levels. Their use is prominent in the production of semiconductors and other sensitive electronic components.
9. Boron Nitride:
Boron Nitride, a unique crucible material composed of boron and nitrogen (BN), offers distinctive advantages in specialized applications. Despite its higher cost, boron nitride crucibles are unparalleled in handling molten metals and non-ferrous materials due to their remarkable properties. With an operating temperature of up to 900°C (1,652°F) in air, boron nitride crucibles excel in scenarios where extreme temperatures are not a primary concern.
Their high chemical stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent thermal conductivity contribute to their effectiveness in ensuring a clean and controlled environment for materials requiring specific handling conditions. While not suitable for applications involving extremely high temperatures, the unique combination of properties makes boron nitride crucibles indispensable in specific niche areas where their characteristics are essential.
Read more: An Overview of Boron Nitride Crucible
10. Tantalum:
Tantalum crucibles, with a high price range, are designed for corrosive and high-temperature environments. With an operating temperature of up to 1,800°C (3,272°F), tantalum crucibles excel in scenarios where corrosion resistance is paramount. Their high cost is justified by their performance in challenging conditions.
Conclusion
In the realm of crucible materials, the choice is never one-size-fits-all. Each material brings its unique set of properties and advantages, catering to specific needs in terms of operating temperature, material compatibility, and budget constraints. As we explored the characteristics of ten popular crucible materials, it became evident that the selection process involves careful consideration of the application's requirements.
For applications demanding a cost-effective yet versatile solution, Clay Graphite crucibles stand out with their moderate price and high operating temperature. Silicon Carbide, with its excellent thermal properties, is a robust choice for environments with rapid temperature changes, though at a slightly higher cost. Graphite, known for its high-temperature resistance and versatility, proves valuable in a range of applications, making it a reliable option for various industries.
While each material has its merits, the final decision must align with the specific demands of the application. The trade-off between price and performance, coupled with an understanding of the material's unique properties, guides the crucible selection process. Whether it be the cost-effective Clay Graphite, the thermal stability of Silicon Carbide, or the high-temperature resilience of Graphite, the key lies in finding the perfect balance to meet the distinct needs of the melting and processing tasks at hand.
At Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM), we take pride in being a leading supplier of high-quality ceramic crucibles for various applications. Contact us today to explore our comprehensive product range and benefit from our expertise in providing innovative solutions for your high-temperature challenges.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments