Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments
Introduction
Ultra-high temperature ceramics are a unique group of materials that keep their form even when heated to more than 1,400°C. Many traditional ceramics tend to break down when temperatures reach these levels. In contrast, these ceramics are built specifically for harsh high-temperature applications. They can help meet tough performance standards, address environmental concerns, and improve production methods.
A Technical Deep Dive into Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics
When you work with materials that must perform in extreme conditions, the details matter. Ultra-high temperature ceramics have been studied and improved over many years. The underlying science is not new, but the practical applications come from a long tradition of trial and error in the lab and in the field. It is not enough to use any ceramic when temperatures soar. These materials have been tweaked over time to resist thermal shock and chemical degradation.
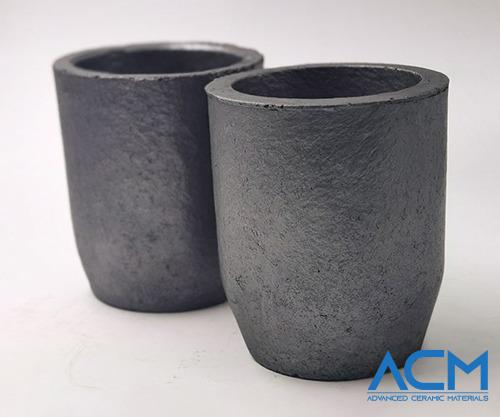
Among the group of ultra-high temperature ceramics, silicon carbide stands out. Its solid performance under stress and heat has made it a reliable choice. Engineers have noted that silicon carbide’s strength, hardness, and ability to conduct heat give it a clear edge over many other materials. In everyday terms, when you need a material that does not bend or lose its shape when things get very hot, silicon carbide answers that call.
Silicon Carbide: A Closer Look
Silicon carbide is not a one-size-fits-all material; it comes in several forms. Its properties vary with the way it is made, which can lead to differences in performance. However, there are some traits that remain constant. Silicon carbide generally offers high strength even after prolonged exposure to heat. Its hardness makes it resistant to wear and abrasion during mechanical contact. The material also has impressive thermal conductivity, which allows it to manage and dissipate heat effectively.
A long history of practical applications backs up silicon carbide’s good qualities. For example, its resistance to corrosion and shock from rapid temperature changes makes it ideal for industrial scenarios where sudden surges in heat occur. Whether in automotive parts, space-bound components, or in chemical processing, silicon carbide has repeatedly proven itself reliable.
Applications of Silicon Carbide in Everyday High-Temperature Environments
Engineers use silicon carbide in a number of settings where the heat is hard to handle. Here are some practical examples:
- Hot Stamping Rollers: In industries that work with hot metal forming, silicon carbide ceramics are used for stamping rollers. The material’s strength at high temperatures helps keep the roller in shape, ensuring a consistent finish on the product.
- Thermocouple Protection Tubes: In furnaces and ovens where temperatures can reach extreme levels, silicon carbide is used to make tubes that shield temperature sensors. This protection is crucial for reliable readings and the safe operation of heat-intensive equipment.
- Temperature Sensors: Some versions of silicon carbide are used to protect temperature sensors in very aggressive environments. With low thermal expansion, these sensors can withstand intense heat without miscalculation.
- Heat Exchangers and Furnace Components: In systems where rapid heat transfer is needed, like heat exchangers and high-temperature furnaces, silicon carbide maintains its integrity and helps regulate temperature. This consistency is of great value in chemical and energy production.
- Semiconductor Equipment: The semiconductor industry relies on materials like silicon carbide for handling delicate wafers. Its chemical inertness means that the material does not contaminate or react with the semiconductor surfaces, ensuring high-quality production.
- New Energy Developments: As new energy solutions take shape, silicon carbide has found a role in parts where thin, high-performance layers are necessary. Whether it is in power electronic components or structural parts of fuel cells, silicon carbide helps achieve performance even when used in layers less than 3 millimeters thick.
Performance and Impact in Industrial Use
When it comes to performance, the numbers back up silicon carbide’s reputation. Research and field tests show that the material retains its strength and shape even under prolonged use. Its resistance to both chemical wear and thermal shock gives industries confidence in its longevity. Routine maintenance becomes easier when key parts do not wear out quickly.
In practical terms, that means fewer shutdowns for repairs and a smoother process line. Companies that deal with high-temperature systems find that using ultra-high temperature ceramics like silicon carbide can save time and money, while keeping equipment in good working order for a much longer period.
Future Developments and Final Remarks
Looking ahead, the use of ultra-high temperature ceramics will likely grow. As industries continue to push the boundaries of what machinery must do, materials that can tolerate extreme conditions will remain in high demand. Continued research will help tweak the properties of ceramics like silicon carbide to meet even tougher requirements. Engineers will continue to use these materials confidently in everything from traditional heavy industries to emerging fields such as renewable energy systems.
In closing, the steady reliability of silicon carbide and its relatives in the ultra-high temperature ceramics family not only ensures consistent performance but also fosters advances that benefit several fields. The trends indicate that these materials will remain integral in industrial settings that require resilience under stress.
For quality ceramics and dependable solutions, consider turning to Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM), a trusted supplier known for their expertise and history in high-performance materials.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments
- Aluminum Oxide Ceramics: Properties and Applications
- Boron Nitride Coatings: The Solution for Molten Metal Applications