Aluminum Oxide Ceramics: Properties and Applications
Introduction
Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), commonly known as alumina, is a technical ceramic known for its reliable mechanical and electrical properties. For many years, this material has served industry with its exceptional strength and durability. Its hard-wearing nature, combined with resistance to wear and chemical attack, makes alumina useful in many demanding environments. The stable thermal performance also ensures that it stands up well under extreme heat, which is important for high temperature applications like thermocouple protection.
Material Grades and Their Characteristics
Alumina comes in several degrees of purity. The three main types are usually classified by their purity percentages: 96%, 99.7%, and 99.95% Ultra Pure.
- The 96% grade is considered a workhorse for many applications. It strikes a good balance between cost and quality. This grade meets the needs of industries where a reliable material is required without overspending on premium purity.
- The 99.7% grade improves upon the electrical insulation and mechanical strength. This makes it more suitable where tighter performance standards are required.
- The 99.95% Ultra Pure grade offers the highest performance with the best mechanical strength, dielectric properties, and thermal conductivity. It is chosen when the most demanding conditions need a material that can provide precise performance.
It's important to note that varying levels of purity can lead to slight changes in density, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity. In applications where any excess wear or short-circuit could cause a big issue, choosing the right grade is very important.
Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties
These purity grades directly translate into a graduated spectrum of measurable properties. The key mechanical, thermal, and electrical characteristics of the primary alumina grades are summarized in the table below:
Table 1: Key Properties of Alumina Ceramics by Purity Grade
| Property | 96% Alumina | 99.7% Alumina | 99.95% Ultra-Pure Alumina |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | ~3.75 | ~3.85 | ~3.98 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | ~2,000 | ~2,600 | ~3,500 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | ~140 | ~170 | ~200 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | ~300 | ~380 | ~450 |
| Hardness (GPa) | ~12 | ~15 | ~18 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | ~25 | ~30 | ~45 |
| Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | >10 | >15 | >20 |
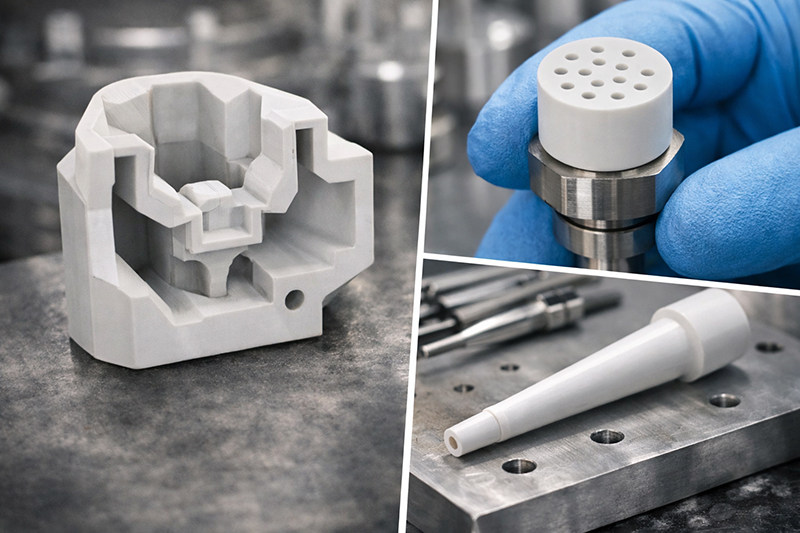
Machining and Fabrication Methods
The outstanding hardness that characterizes alumina's performance also determines its specialized machining and fabrication methods. During the early "green" stage, the material can be shaped into various forms. This allows it to be processed into different sizes and configurations, which is useful for custom applications. Once it undergoes the sintering process and achieves its full density, it experiences a reduction in size by about 20%. At this stage, tight tolerances can only be achieved by using diamond tools for grinding the material down to exact dimensions.
The machining steps include:
- Injection molding, die pressing, and isostatic pressing for standard shapes
- Slip casting and extrusion for producing more complex profiles
- Diamond grinding to refine the final shape once the material is fully sintered
These methods show that while alumina is a hard material to work with, there are established practices that ensure a high level of precision for critical parts.
Advantages and Applications
Alumina holds many advantages. Its very high hardness and resistance to abrasion allow it to handle mechanical stress and wear. In addition, alumina offers excellent electrical insulation. It excels in resisting strong acids and alkaline conditions under high-temperature exposure. Because of these traits, alumina is often chosen for parts that must keep their form and function over long periods or under harsh conditions.
Common uses include:
- Electronic components and substrates
- High-temperature insulators for both industrial and laboratory use
- Mechanical parts like pistons and sleeves in engines or pumps
- Components within high voltage systems
- Wear parts in applications needing resistant inserts
- Items used in semiconductor processing and laser tubes
Practical Considerations in Use
When designing with alumina, it is important to keep in mind its many advantages balanced against its challenges. While its high durability, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical attack make it ideal for many applications, the material is also tougher to machine. This means that production costs can be higher for small batches or detailed parts when compared to more easily processed materials.
Engineers and technicians must account for shrinkage during sintering and carefully manage the machining process using appropriate tools. A good understanding of the material's properties and behavior during processing is key to a successful outcome.
Conclusion
Decades of proven performance have solidified alumina's status as a benchmark material in the ceramics family. Their excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical insulation capabilities have proved valuable in high-wear and high-temperature environments. Whether used for electronic components, high-temperature insulators, or wear-resistant machine parts, alumina remains a trusted material for many modern challenges.
For those looking to source high-quality alumina or require expert advice on technical ceramic manufacturing, Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) stands ready to offer experience and support to meet your specialized needs.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments














